Taking a Macroscopic Perspective of Data Management
In the realm of decision-making, data plays a pivotal role, making it essential to adopt a broader perspective when it comes to Data Management. This means looking at individual processes as integral components of a larger system. This bird’s-eye view of the entire system is instrumental in pinpointing areas for improvement. By implementing targeted measures, we can enhance the reliability of data and the efficiency of the system.
Data Management encompasses two core elements: Data Pipelines and Data Governance.
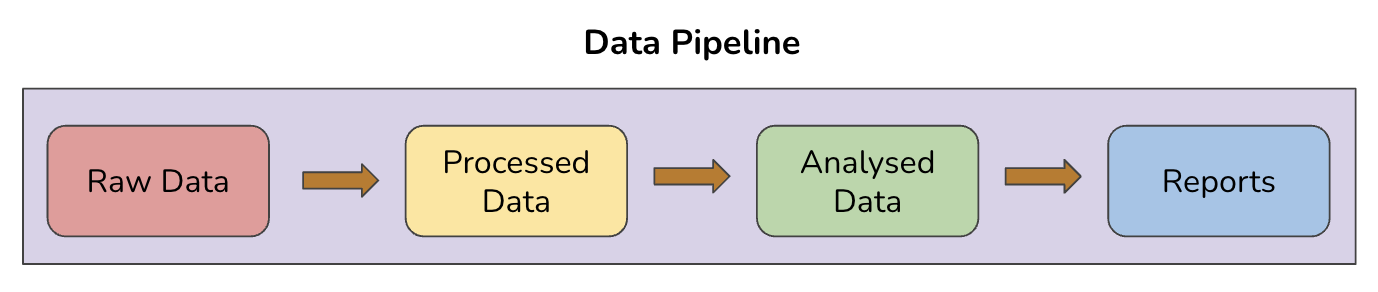
Data Pipelines serve as the foundational infrastructure for data management. They encompass a series of stages that data traverses, from its initial collection to its ultimate utilisation.
- Data Collection: At this stage, raw data is sourced from various origins using diverse methods. This could involve gathering data from existing databases or published sources, or collecting information through field surveys conducted by individuals or online forms like Google Forms.
- Data Cleaning and Processing: Raw data often arrives with errors, inconsistencies, and missing values. Data cleaning and processing are essential for ensuring data accuracy and readiness for analysis.
- Data Analysis: This phase involves extracting meaningful insights from the processed data. Statistical techniques are employed to identify patterns, trends, and correlations within the data.
- Reporting: The results of data analysis must be presented in a format that is comprehensible and valuable to decision-makers. This could take the form of reports, dashboards, or other visualisations.
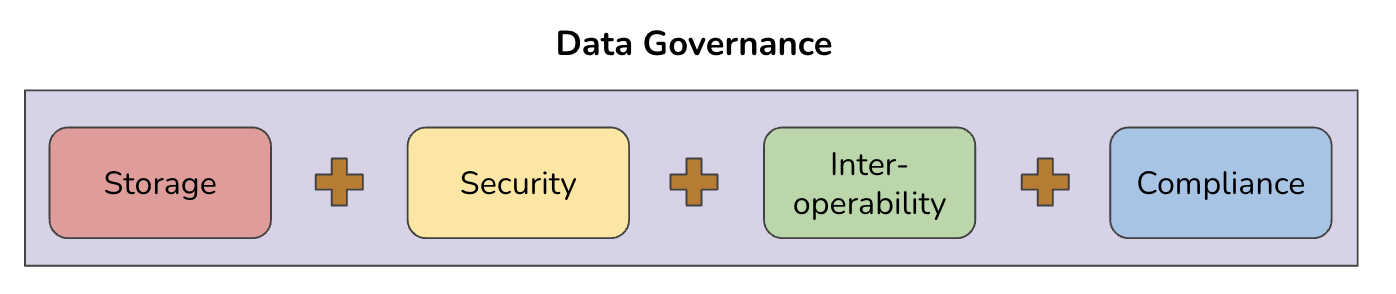
Data Governance, on the other hand, is a comprehensive framework that governs and supervises data-related activities. It encompasses crucial processes such as data storage, data security, data interoperability, and data compliance.
- Data Storage: Decisions regarding where and how data is stored are important, considering that data needs to be available not just for decision-making in the present but also for archival and reference purposes in the future.
- Data Security: This involves safeguarding data from unauthorised access, breaches, and cyber threats. Implementing encryption, access controls, and conducting regular security audits are vital steps in this regard.
- Data Interoperability: Ensuring that data can be efficiently exchanged and integrated across different systems is crucial. This necessitates standardisation and effective metadata management so that data can be shared both within and across organisations.
- Data Compliance: Ensuring that data usage adheres to relevant regulations, policies, and government-specific data protection laws is an essential and often overlooked part of data governance.
By adopting this macroscopic approach to Data Management, organisations and government departments can optimise their data-related processes and better serve their decision-making needs.